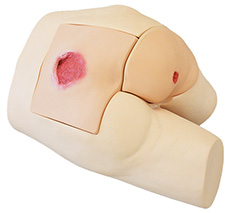
Pressure Sores Simulator - MW63 - Kyoto Kagaku
MW63 Pressure Sores Simulator is a decubitus care skills trainer for the new era. Its detailed representation allows for a wide range of training scenarios, including sore assessment , ultrasound assessment of deep tissue injury, and necrotic tissue removal.
Features- Assessment of Pressure Sores
- Compatible with DESIGN-R 2020
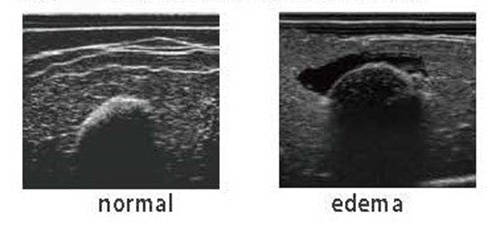
- Assessment of deep tissue by ultrasound
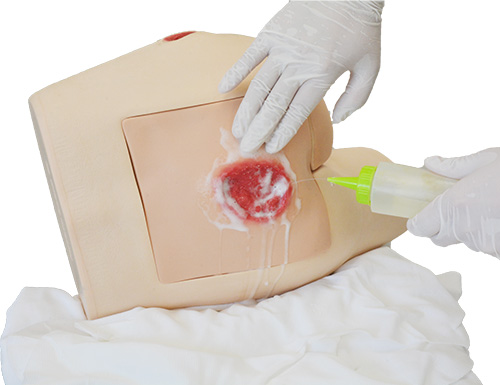
- Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers / Cleansing /Dressing
- Realistic reproduction of human tissue allows for accurate training environment
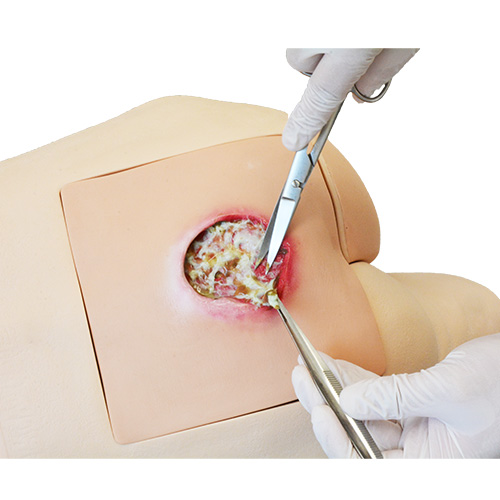
- assessment / palpation / ultrasound assessment of sciatic area / cleaning / dressing / application of topical medication/ NPWT/ debridement of necrotic tissue
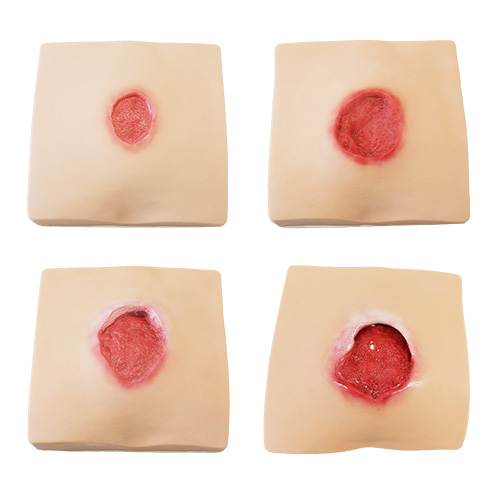
- sacral pressure sore (4 types)
- greater trochanter pressure sore
- sciatic pressure sore (3 types including deep tissue injury)
- 1 lower body torso
- 4 types of sacral pressure sore pads (stage II, stage III, stage IV with granulation and stage IV with pockets)
- 1 sciatic pressures sore pad
- 2 types of echo pads
- 1 necrotic tissue removal set
- 1 consumable set (simulated pus, blood, exudate and necrotic tissue)
- 1 storage case
- 1 instruction manual
- 1 lower body torso
- 4 types of sacral pressure sore pads (stage II, stage III, stage IV with granulation and stage IV with pockets)
- 1 sciatic pressures sore pad
- 1 consumable set (simulated pus, blood, exudate and necrotic tissue)
- 1 storage case
- 1 instruction manual
Size (approx.)
- W44×D40×H38cm
- W52x D49x H29㎝/W20.5x D19x H11.5in
- 3.8kg
- 11446-010 consumable set
- 11446-020 simulated pus (set of 2 packs)
- 11446-030 simulated exudate (set of 2 packs)
- 11446-040 simulated blood (set of 2 packs)
- 11446-050 simulated necrotic tissue (set of 2 packs)
- 11446-200 necrotic tissue removal set
- 11446-070 echo pads set (normal/edema)
- MD. PhD, Professor Hiroto Terashi , Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery , Kobe University School of Medicine
- Masaharu Sugimoto, Former Professor, Kobe Gakuin University
- Madoka Noguchi, Nursing Department, Kobe University Hospital